Redis2.2.2源码学习——dict中的hashtable扩容跟rehash
日期:2014-05-16 浏览次数:20521 次
Redis2.2.2源码学习——dict中的hashtable扩容和rehash
Redis2.2.2
dict是Redis的hash数据结构,所有类型的元素都可以依据key值计算hashkey,然后将元素插入到dict的某个hash链上(采用拉链法解决hash冲突)。其中,dict的中的hashtable(dictht)的扩容是dict很重要的部分。Redis的“管家”函数serverCron会依据一定的算法(dict中的used与size的比值)判定是否开始进行hashtable的扩容。dict中的ht[1]是作为扩容的临时数据,扩容之后,hashtalbe的长度将变长,那么hashtalbe的masksize与原来的makssize就不同了,那么计算出的hashkey也将不同。所以就需要Rehash对ht[0]中的元素重新计算hashkey。
在Rehash阶段,首先将原来的ht[0]中的元素重新rehash到ht[1]中,故而要耗费大量的力气从新计算原来的ht[0]表中元素的在ht[1]表总的hashkey,并将元素转移到ht[1]的表中。由于这样Rehash会耗费大量的系统资源,如果一次性完成一个dict的Rehash工作,那么将会对系统中的其他任务造成延迟? 作者的处理方式是:同样在serverCron中调用rehash相关函数,1ms的时间限定内,调用rehash()函数,每次仅处理少量的转移任务(100个元素)。这样有点类似于操作系统的时间片轮转的调度算法。
下图是Dict相关数据结构(引用: Redis源码剖析(经典版).docx )
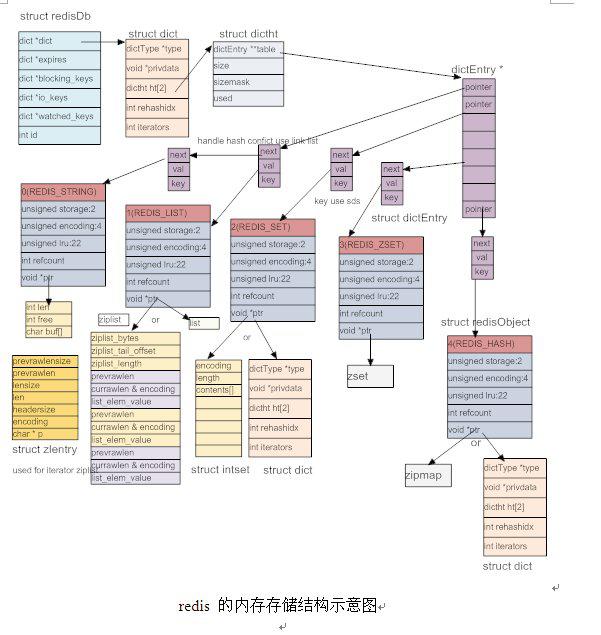
代码分析如下:
-----------------------Data Sturcter----------------------------------------
typedef struct dictEntry {
void *key;
void *val; //空类型,redis的类型主要有sds,list,set等,val指针指向其中的结构
struct dictEntry *next;
} dictEntry;
typedef struct dictType {
unsigned int (*hashFunction)(const void *key);
void *(*keyDup)(void *privdata, const void *key);
void *(*valDup)(void *privdata, const void *obj);
int (*keyCompare)(void *privdata, const void *key1, const void *key2);
void (*keyDestructor)(void *privdata, void *key);
void (*valDestructor)(void *privdata, void *obj);
} dictType;
/* This is our hash table structure. Every dictionary has two of this as we
* implement incremental rehashing, for the old to the new table. */
typedef struct dictht {
dictEntry **table;//hash表,每个table[i]链表存储着一个hashkey相等的dictEntry指针
unsigned long size;//table[]的大小
unsigned long sizemask;// = size-1
unsigned long used;//当前table中存储的dictEntry指针的个数
} dictht;
typedef struct dict {
dictType *type;//hash相关的操作hander
void *privdata;
dictht ht[2];//ht[0]作为dict的实际hash结构,ht[1]做为扩容阶段的转储结构
int rehashidx; //标志dict是否处于rehash阶段,如果值为-1,表示不处于rehash。否则,在rehash中所谓hashtalbe的索引下标
int iterators; /* number of iterators currently running */
} dict;
------------------------Redis's main----------------------------------------
main() >
initServerConfig()
server.activerehashing = 1;
initServer()
//设置定时事件,1ms调用一次serverCron()
aeCreateTimeEvent(server.el, 1, serverCron, NULL, NULL);
//进入事件轮询,详见:http://blog.csdn.net/ordeder/article/details/12791359
aeMain(server.el)
------------------------serverCron-----------------------------------------
/*serverCron是Redis的协调员,其中就包括:
1.检查是否有hashtalbe需要扩容,并执行必要的扩容
2.执行incrementRehash执行固定时间的Rehash任务
*/
int serverCron(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop, long long id, void *clientData)
/*记录sever调用serverCron的总次数
*对于需要协调的不同的任务,可以依据loops%n的方式设置不同的频率 */
int loops = server.cronloops
。。。
/* We don't want to resize the hash tables while a bacground saving
* is in progress: the saving child is created using fork() that is
* implemented with a copy-on-write semantic in most modern systems, so
* if we resize the HT while there is the saving child at work actually
* a lot of memory movements in the parent will cause a lot of pages
* copied. 后台没有对数据进行操作的程序...*/
if (server.bgsavechildpid == -1 && server.bgrewritechildpid == -1) {
/*loops % 10 :
serverCron没循环10次,进行一次tryResizeHashTables检查*/
if (!(loops % 10)) tryResizeHashTables();
//下面的for是tryResizeHashTables源码
>for (j = 0; j < server.dbnum; j++) {
//htNeedsResize:检查used*100/size < REDIS_HT_MINFILL(设定的阈值)
if (htNeedsResize(server.db[j].dict))
dictResize(server.db[j].dict);//见下文分析 扩容Resize
if (htNeedsResize(server.db[j].expires))
dictResize(server.db[j].expires);
>}
if (server
免责声明: 本文仅代表作者个人观点,与爱易网无关。其原创性以及文中陈述文字和内容未经本站证实,对本文以及其中全部或者部分内容、文字的真实性、完整性、及时性本站不作任何保证或承诺,请读者仅作参考,并请自行核实相关内容。
